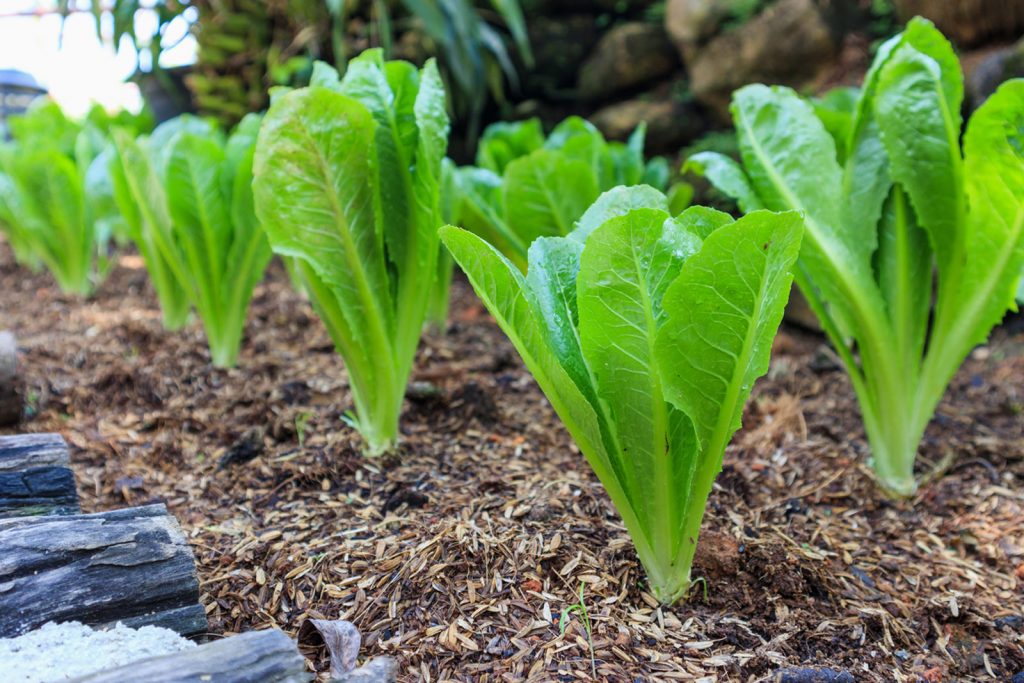
Lettuce farming is gaining popularity day by day. It is among the highest consumed salad vegetable throughout the world. Becoming trendy in India too.
Although the roots of lettuce farming lie in Asia. Though, it was wholehearted adopted by the rest of the countries.
Being a store of healthy nutrients, how to grow lettuce, became an important part of farming.
The Romaine species of lettuce is the most famous among all. Lettuce finds a place in healthy food items like wraps, salads, sandwiches. Etc.
China lead in the production of lettuce. It is a spiral leafy vegetable with a package of health.
This crop has acquired commercial importance in the passage of time. If you are planning a business strategy by growing lettuce, surely will land towards wealth in your bag.
How grab a look!!!!!
Different types of lettuce
These nutrition ruched salad leaves have different species. Check them out:
- Leaf Lettuce:
They are like a branch splashing out from the stalk. Red, green, and Oak in color. Leaf lettuce is the most delicate and short-lived. The red one has a mild flavor than the green one. While the oak one is the crunchiest and spiciest.
- Romaine Lettuce:
Sweet in center and bitterly towards the tip, long and firm in appearance.
- Iceberg lettuce:
It is crispy in taste and resembles cabbage. Unlike lettuce, it is not juicy. Can be refrigerated for 15 days in plastic bags.
- Arugula Lettuce:
This is generally used in pizza toppings. Blends with pesto sauce so go well in sandwiches too.
- Frisse:
It belongs to the radicchio family. Available in grocery stores are used as toppings.
Requirements for how to grow lettuce
For growing lettuce on your farm, these things should not be overlooked. Note the following:
Climate
Being a cool-headed crop thrives amazingly well at temperatures ranging between 15 to 18 degrees.
They are reluctant towards extremely hot temperatures. It can be cultivated throughout the year using shady or greenhouse effect in warmer climates.
They have a speedy growth. And performs well in the spring season. Ideally, the lettuce growing season is spring time before the onset of scorching heat.
Soil Required
Good organically rich soil is a perfect combo for Lettuce cultivation. The soil should excel in two things, water retention and good drainage.
This is a boon in disguise for farming. Highly allergic to acidic soil, better to choose a neutral one.
Prepare Land
The land needs good plowing till tilth. Plowing has to be carried out for successive 3-4 times.
Also, get the soil tested for productivity and if needed add some good organic manure to boost up the productivity.
Make necessary arrangements to flush out excessive water at frequent intervals.
Irrigation
Water supply should be maintained regularly. For this, you can water the plantation, once every 4 days. Extra water must be flushed out during excessive rains.
Fertilization
60 TO 65 KG of potash and phosphorus is needed by the lettuce crop. With good quantity of manure around 15 to 20 tonnes. It ensures healthy growth.
Pest and Disease Control
The pests are the disturbance-causing agent. They hamper the yield and have an adverse effect on lettuce cultivation.
Cutworms, bollworms, aphids are some of the enemies of the lettuce plantation. Soft rot, downy mildew are the diseases caused by these agents.
To curb their spread, you need to approach the horticulture department for some remedy.
Germination in lettuce seeds
Lettuce seed germination is an easy process. But you don’t have to be antsy. Pick the best quality seeds from the market or any other reliable source.
Now plant these seeds in the soil. The temperature of the place is the deciding factor to initiate lettuce seed germination.

Make sure the temperature is 20 degrees at least. Else, the seeds will enter a deep sleep mode.
During the entire sprouting time, these standards should be maintained. Ideal temperature, exposure to sunlight, and moisture laden soil is an explicit combo to trigger sprouting in seeds.
This has to be maintained for 7 to 10 days until the germination starts. You can see tiny tots emerging from the seeds.
How to grow lettuce from seeds
Propagation through seeds is easy. You can sow them directly into the soil. As an alternative, they can be planted in a nursery till germination.
After that, it can be translocated to the fields.

Mostly leafy varieties are cultivated by this method. Raised beds are prepared in the field. This ensures proper water drainage and air to the soil.
The seeds should be at least 12 to 15 mm deep. This is ideal, depth for a lettuce plantation.
A lettuce plant spacing should be done in rows 15 to 25 cms far from each other.
Also Read: How To Plant Spinach? Here Is Everything You Need To Know
How to grow leaf lettuce from seed
Leaf lettuce demands sunlight, although too much heat can be injurious. Causing bolting of leaves. As an introductory step, sow the seeds inside for about 4 weeks before the arrival of frost.
Amid springs, shift them outside in the fields. The purpose is to allow a shady and light sun area till the germination process pops up.
Do make a note sun is an essential element to instigate germination. So, don’t sow them very deeply. And cover with a thin layer of soil to allow the sunlight to reach them.
The soil quality of those freshly prepared beds should be highly productive and the PH between 6.2 to 6.8. Acid or lime soil burns the seeds. The soil must be moisture-laden to keep nurturing the seeds.
Spacing style is like one-inch gap between the seeds and a 12 to 18 inches gap between the soil beds or rows.
Before shifting the sprouting seeds allow the seeds to get harder by reducing the water content. Maintain the temperature of 20 degrees.
Then translocate them to their soil beds in fields. Water them and protect them from injuries by moths and bugs.
After some time they start growing, keeping mulching the soil to retain the fertility. Once lettuce farming starts flourishing, it’s time to remove them before the frost arrives.
Harvesting lettuce
Such a delightful sight it is, to have those butter surfaced, big green crunch in the field waiting for you. Firstly, when to harvest lettuce is not restricted to the maturity stage.
Lettuce can be removed at any point in time. As it is consumable at every stage of growth. Even small leaves are demanded in the market for sandwiches, wraps, etc.

Always pluck lettuce in the early hours of the day before sunlight falling on them. To enjoy the lettuce thickens, pluck the early tiny leaves and allow the plant to grow densely.
Allow the plant to attain a bigger size. When to feel the firmness of leaves, then it’s perfect time to get the juicy leaves out. When and how to harvest lettuce is all about the firmness of the plant.
As it can be plucked anytime.
Benefits of the lettuce plant
Consumption of lettuce can be beneficial in multiple ways. Having a calorie content of 12, it is highly recommended for weight loss.
Fibrous and cellulose riches make it desirable. It assists in the breakdown of cholesterol.
Makes you hail and hearty. Strengthens the functioning of the heart.
Storehouse for omega-rich fatty acids.
Work on the protein deficiency in the body.
Conclusion
This was a brief insight into how to grow lettuce. Once you start your lettuce farming, you will get to know the profitability of this venture.
Starting the business and setting your goal towards a decent profit earning, depends on the number of efforts invested in it.
Apart from this, you have a clear picture of how much trendy lettuce has become these days.
In comparison to older times where it was considered as a fancy or lavishly consumed vegetable. Now it finds a way to the routine diet of people.
With the above information, you are already a step ahead towards lettuce farming.
Start growing your lettuce for a profitable venture.